|
|
➳
Apr 1, 2021 12:07:55 GMT
Post by Admin on Apr 1, 2021 12:07:55 GMT
.  |
|
|
|
➳
Apr 1, 2021 12:23:22 GMT
Post by Admin on Apr 1, 2021 12:23:22 GMT
.  On the ceiling of the lantern, which rises above the highest part of the dome, is a painting of a beautiful female figure representing Human Understanding, ( Wisdom ) in the act of lifting the veil of ignorance and looking forward to intellectual progress
She is attended by two cherubs: one is holding the book of wisdom and knowledge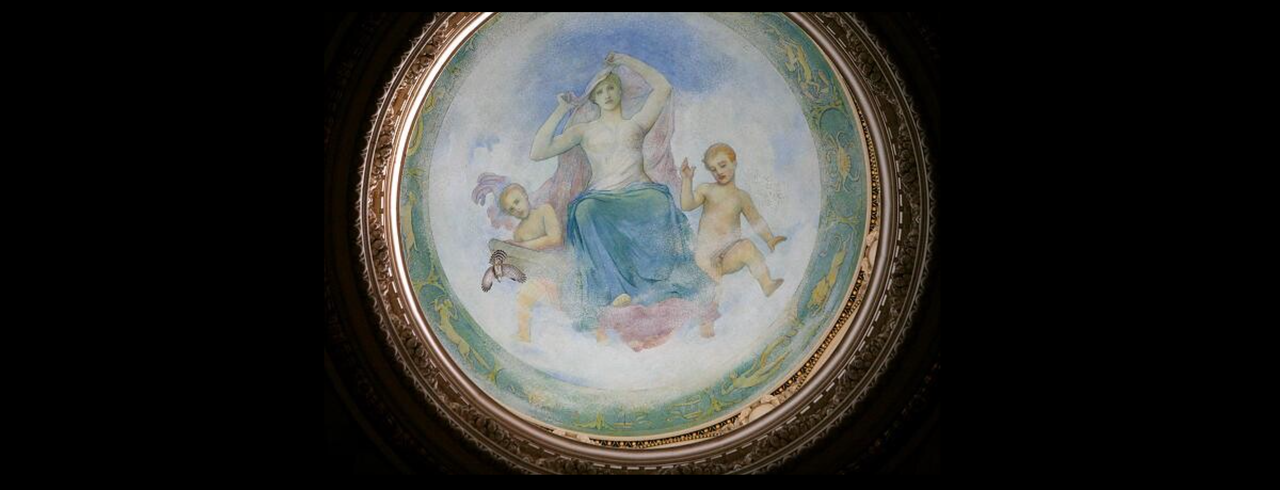  She is surrounded by the 12 constellations of the Zodiac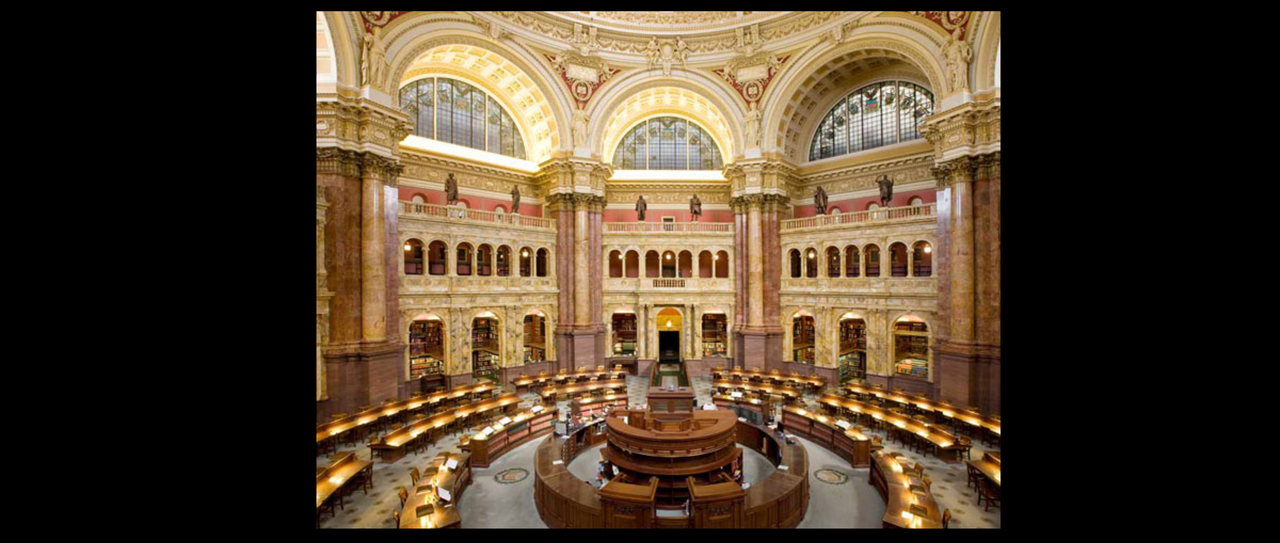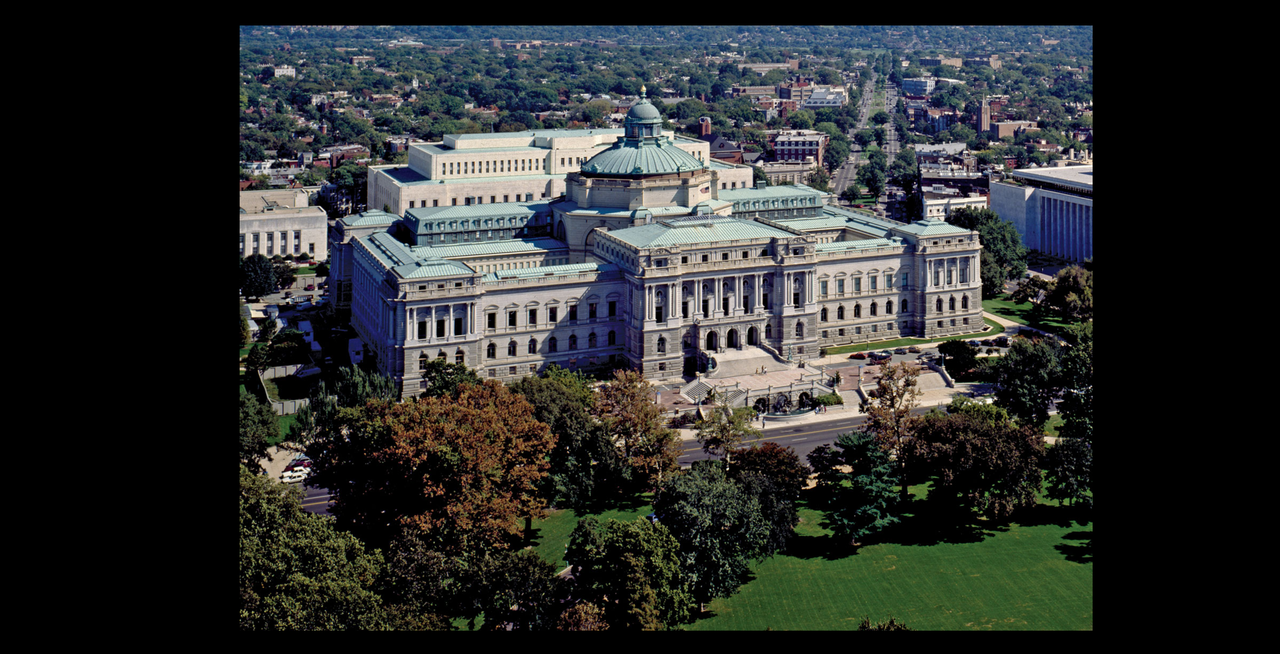     In Greek mythology, a little owl (Athene noctua) traditionally represents or accompanies Athena, the virgin goddess of wisdom, or Minerva, her syncretic incarnation in Roman mythology. Because of such association, the bird—often referred to as the "owl of Athena" or the "owl of Minerva"—has been used as a symbol of knowledge, wisdom, perspicacity and erudition throughout the Western world Athena the Virgin, patron saint of Athens  |
|
|
|
➳
Apr 6, 2021 6:40:02 GMT
Post by Admin on Apr 6, 2021 6:40:02 GMT
. 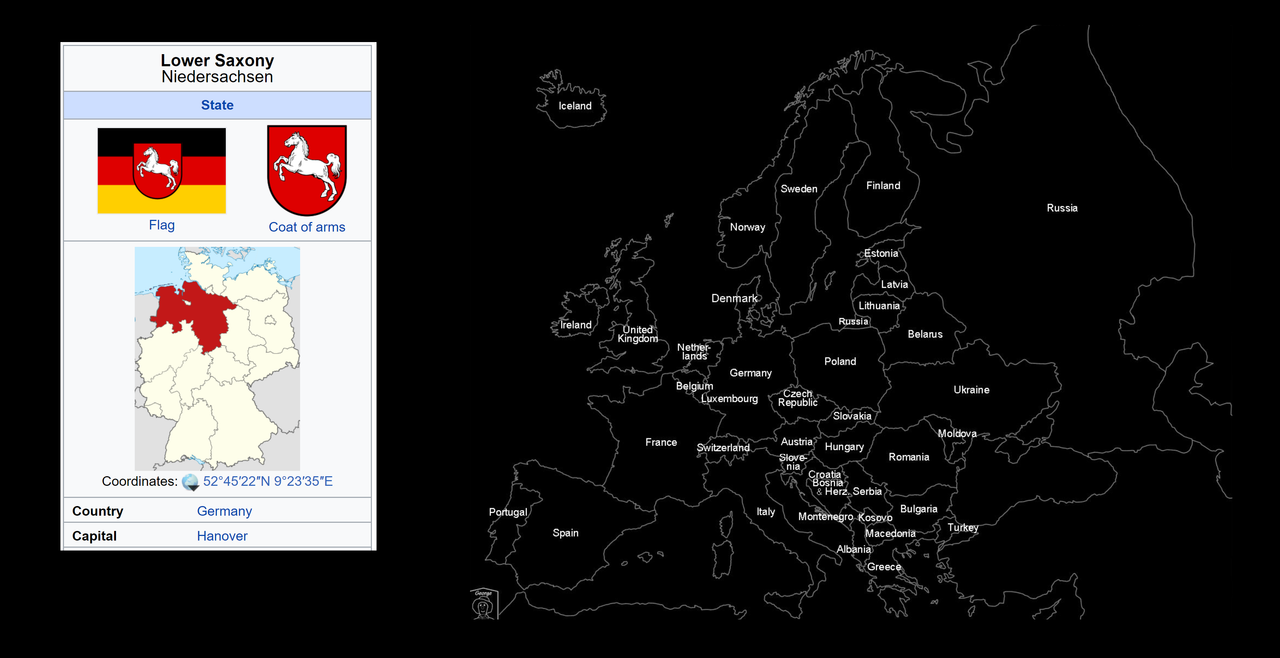 The name and coat of arms of the present state go back to the Germanic tribe of Saxons. During the Migration Period some of the Saxon peoples left their homeland in Holstein about the 3rd century and pushed southwards over the Elbe, where they expanded into the sparsely populated regions in the rest of the lowlands, in the present-day Northwest Germany and the northeastern part of what is now the Netherlands. From about the 7th century the Saxons had occupied a settlement area that roughly corresponds to the present state of Lower Saxony, of Westphalia and a number of areas to the east, for example, in what is now west and north Saxony-Anhalt. The land of the Saxons was divided into about 60 Gaue. The Frisians had not moved into this region; for centuries they preserved their independence in the most northwesterly region of the present-day Lower Saxon territory. The original language of the folk in the area of Old Saxony was West Low German, one of the varieties of language in the Low German dialect group The word Niedersachsen was first used before 1300 in a Dutch rhyming chronicle (Reimchronik). From the 14th century it referred to the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (as opposed to Saxe-Wittenberg) The House of Windsor is the reigning royal house of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms. In 1901, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (a branch of the House of Wettin) succeeded the House of Hanover to the British monarchy with the accession of King Edward VII, son of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. In 1917, the name of the royal house was changed from the anglicised German Saxe-Coburg and Gotha to the English Windsor because of anti-German sentiment in the United Kingdom during World War I. There have been four British monarchs of the House of Windsor since then: George V, Edward VIII, George VI, and Elizabeth II The House of Hanover (German: Haus Hannover), whose members are known as Hanoverians, is a German royal house that ruled Hanover, Great Britain, and Ireland at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. The house originated in 1635 as a cadet branch of the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, growing in prestige until Hanover became an Electorate in 1692. George I became the first Hanoverian monarch of Great Britain and Ireland in 1714. At Victoria's death in 1901, the throne of the United Kingdom passed to her eldest son Edward VII, a member of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The last reigning members of the House lost the Duchy of Brunswick in 1918 when Germany became a republic The formal name of the house was the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Hanover line The senior line of Brunswick-Lüneburg, which ruled Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, became extinct in 1884. The House of Hanover is now the only surviving branch of the House of Welf, which is the senior branch of the House of Este The House of Este was an Italian princely family, linked with several contemporary royal dynasties, including the House of Habsburg and the British royal family The elder branch of the House of Este, known as the Younger House of Welf, included dukes of Bavaria and Brunswick-Lüneburg and produced Britain's Hanoverian monarchs, as well as one Emperor of Russia (Ivan VI) and one Holy Roman Emperor (Otto IV) According to Edward Gibbon, the family originated from the Roman Attii family, which migrated from Rome to Este to defend Italy against the Ostrogoths. However, there is little evidence to support this hypothesis The names of the early members of the family indicate that a Frankish origin is much more likely============ Notes |
|
|
|
➳
Apr 6, 2021 6:48:14 GMT
Post by Admin on Apr 6, 2021 6:48:14 GMT
The Merovingian dynasty (/ˌmɛrəˈvɪndʒiən/) was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751 They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaulish Romans under their rule. They conquered most of Gaul, defeating the Visigoths (507) and the Burgundians (534), and also extended their rule into Raetia (537). In Germania, the Alemanni, Bavarii and Saxons accepted their lordship. The Merovingian realm was the largest and most powerful of the states of western Europe following the breaking up of the empire of Theoderic the Great The dynastic name, medieval Latin Merovingi or Merohingii ("sons of Merovech"), derives from an unattested Frankish form, akin to the attested Old English Merewīowing, with the final -ing being a typical Germanic patronymic suffix. The name derives from King Merovech, whom many legends surround. Unlike the Anglo-Saxon royal genealogies, the Merovingians never claimed descent from a god, nor is there evidence that they were regarded as sacred The Carolingian dynasty (known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family founded by Charles Martel with origins in the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD The dynasty consolidated its power in the 8th century, eventually making the offices of mayor of the palace and dux et princeps Francorum hereditary, and becoming the de facto rulers of the Franks as the real powers behind the Merovingian throne. In 751 the Merovingian dynasty which had ruled the Germanic Franks was overthrown with the consent of the Papacy and the aristocracy, and Pepin the Short, son of Martel, was crowned King of the Franks. The Carolingian dynasty reached its peak in 800 with the crowning of Charlemagne as the first Emperor of Romans in the West in over three centuries. His death in 814 began an extended period of fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and decline that would eventually lead to the evolution of the Kingdom of France and the Holy Roman Empire The Quinotaur (Lat. Quinotaurus) is a mythical sea creature mentioned in the 7th century Frankish Chronicle of Fredegar. Referred to as "bestea Neptuni Quinotauri similis", (the beast of Neptune which resembles a Quinotaur) it was held to have fathered Meroveus by attacking the wife of the Frankish king Chlodio and thus to have sired the line of Merovingian kings The name translates from Latin as "bull with five horns", whose attributes have commonly been interpreted as the incorporated symbols of the sea god Neptune with his trident, and the horns of a mythical bull or Minotaur. It is not known whether the legend merged both elements by itself or whether this merger should be attributed to the Christian author The clerical Latinity of the name does not indicate whether it is a translation of some genuine Frankish creature or a coining The suggested rape and subsequent family relation of this monster attributed to Frankish mythology correspond to both the Indo-European etymology of Neptune (from PIE '*nepots', "grandson" or "nephew", compare also the Indo-Aryan 'Apam Napat', "grandson/nephew of the water") and to bull-related fertility myths in Greek mythology, where for example the princess Europa was abducted by the god Zeus, in the form of a white bull, that swam her to Crete; or to the very myth of the Minotaur, which was the product of Pasiphaë's, a Cretan Queen's, intercourse with a white bull, initially allotted to King Minos, Pasiphaë's husband, as a sacrifice for Poseidon  ============= Notes cf red and white in history of red |
|
|
|
➳
Apr 6, 2021 6:59:57 GMT
Post by Admin on Apr 6, 2021 6:59:57 GMT
.  Troyes, France Troyes has been in existence since the Roman era, then known as Augustobona Tricassium, which stood at the hub of numerous highways, primarily the Via Agrippa  |
|